Abstract
Background: The prognosis of relapsed/refractory (R/R) myeloid malignancies remains poor, and the development of novel treatment strategies is crucial. Although chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified T cell therapy for B cell malignancies has shown excellent clinical efficacy, the use of CAR-T cells for myeloid malignancies has been more challenging, partly due to the heterogeneous expression of candidate target antigens in leukemia cells and shared expression of those antigens in normal myeloid cells or progenitor cells. We previously developed the piggyBac-modified chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells targeting CD116, also known as GM-CSF receptor alpha chain (GMR) (Nakazawa Y, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2016 and Hasegawa A, et al. Clin Transl Immunology. 2021). GMR CAR-T cells showed substantial antitumor effects against both acute myeloid leukemia and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Moreover, modulation of the spacer and antigen recognition site of the CAR vector further enhanced the anti-tumor effects of GMR CAR-T cells. GMR CAR-T cells showed an acceptable safety profile with limited cytotoxicity on normal hematopoietic cells except monocytes. Based on these results, we have initiated a first-in-human clinical trial of GMR CAR-T cell therapy in March 2021 in Japan.
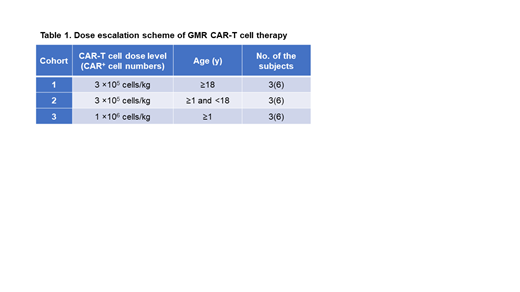
Study Design and Methods: The study is a phase I/II, single-center, dose-escalation study with a traditional 3+3 dose-escalation design (Table 1). Maximum of 18 patients will be recruited. Primary objectives of this study are to determine the safety and severe adverse events of piggyBac-modified GMR CAR-T cells for CD116 + relapsed/refractory myeloid malignancies by assessing the dose-limiting toxicity within 28 days from the single infusion of GMR CAR-T cells.
The patients with CD116 + myeloid malignancies aged more than 1 year with myeloid malignancies who experienced an induction failure or a relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) will be recruited. CD116 is defined as positive when a CD116 relative mean fluorescence (RFI) in leukemia cells ≥ 2. RFI was calculated by dividing the MFI of samples with that of the isotype control. Major exclusion criteria are as follows, acute promyelocytic leukemia, acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (Grade ≥ 2), extensive chronic GVHD, and concurrent treatment with corticosteroid (≥ 6 mg/m2). Statistical analysis will be performed when the data will be fixed.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells will be harvested from the patient by leukapheresis and then will be transduced with GMR CAR vector by piggyBac transposon system. All manufacturing process of GMR CAR-T cells is performed in Cell Processing Center in Shinshu University Hospital under good manufacturing practice conditions. The patient will be treated with lymphodepleting chemotherapy consisting of fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by CAR-T cell infusion. The dose of CAR-T cells will be 3 x 10 5 and 1 x 10 6 in cohorts 1 & 2 and cohort 3, respectively (Table 1). Kinetics of GMR CAR-T cells will be determined by quantifying the GMR CAR gene in the peripheral blood using real-time PCR after the CAR-T cell infusion. All the patients will be required to receive HSCT by day 56 following CAR-T cell infusion. The primary endpoint of the study is the safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of GMR CAR-T therapy (Trial registration: jRCT2033210029).
Conclusion: We herein described the protocol of first-in-human GMR CAR-T cells for relapsed/refractory myeloid malignancies. By employing the optimized CAR vector and production protocol, the safety and efficacy of GMR CAR-T cells will be evaluated in this study.
Saito: Toshiba corporation: Research Funding. Yagyu: AGC Inc.: Research Funding. Nakazawa: AGC Inc.: Research Funding; Toshiba Corporation: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal